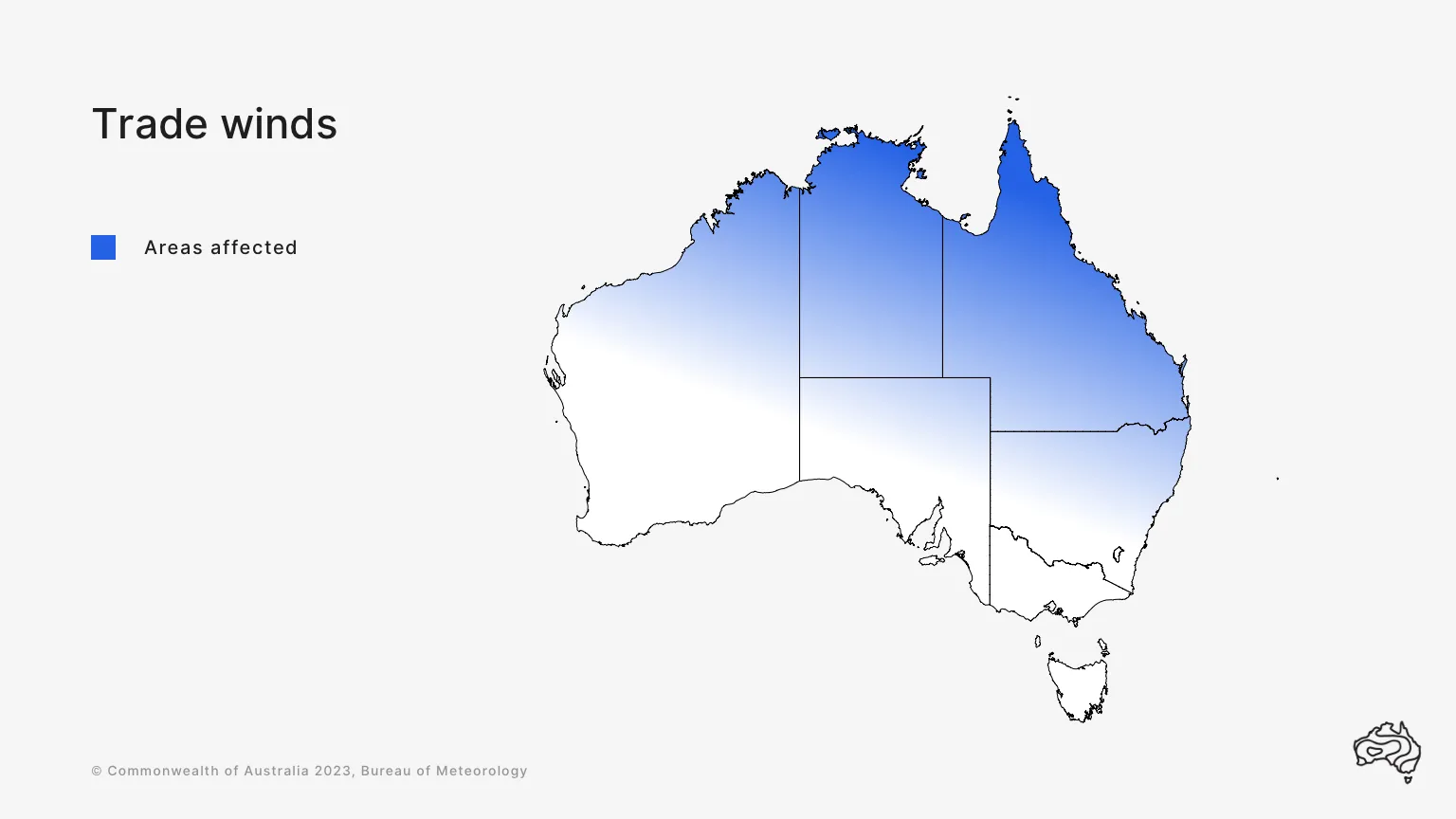
What are trade winds?
Trade winds are prevailing winds in the Earth's tropics. They blow from east to west all year. This is part of the general circulation of the Earth's atmosphere.
In the southern hemisphere, the trade winds are east to south-easterly. They affect the climate in tropical and subtropical areas of Australia.
Location of the trade winds
The trade winds blow across the tropics both north and south of the equator.
They blow east to west between the equator and a band of high pressure systems in the middle latitudes, called the subtropical ridge.
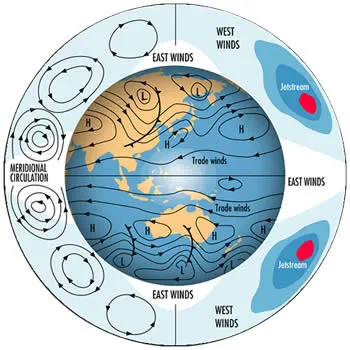
Trade winds in the southern hemisphere blow east to west above a band of high pressure systems
How trade winds affect Australia
The trade winds affect much of Australia's north and parts of its east.
The winds collect moisture as they move east, over the tropical Pacific Ocean. The moist wind enhances rainfall in tropical and sub-tropical areas of our east coast.
Southern winter – Northern dry season
The trade winds are strongest during the winter months. This is dry season in the tropics.
In northern Australia, the monsoon moves to the northern hemisphere. The winds lose moisture as they move over inland northern Australia and the top end. This brings more stable and drier conditions to these areas of the country.
Southern summer – Northern wet season
In the summer months, the subtropical ridge moves south. The trade winds weaken and the monsoon returns to northern Australia.
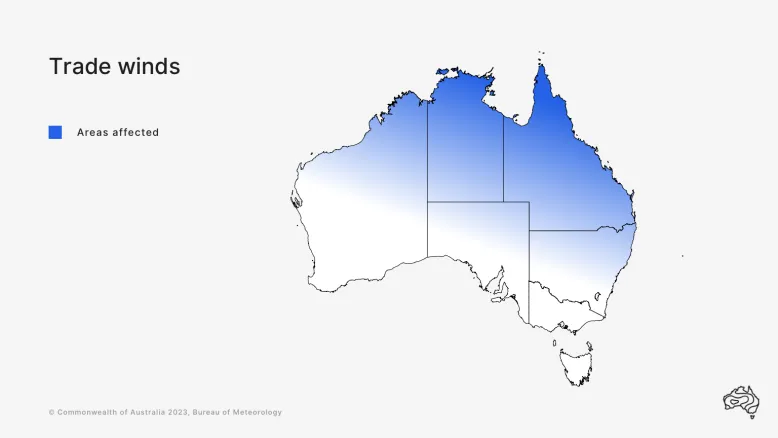
The trade winds blow all year round but are strongest in the winter months. They enhance rainfall over tropical and subtropical parts of eastern Australia.
Weather and climate factors related to trade winds
East coast lows and easterly troughs
East coast lows and easterly troughs can disturb the flow of trade winds.
Cold fronts
The regular winter pattern of cold fronts across southern Australia can also affect trade winds.
El Niño and La Niña
Variations in the strength of the trade winds also affect the tropical Pacific Ocean during El Niño and La Niña events.
Monsoon
The trade winds interact with the monsoon. They can affect the location and strength of the trough. This affects where widespread rain occurs over northern Australia.
Subtropical ridge
The subtropical ridge forms a southern boundary to the trade winds south of the equator.