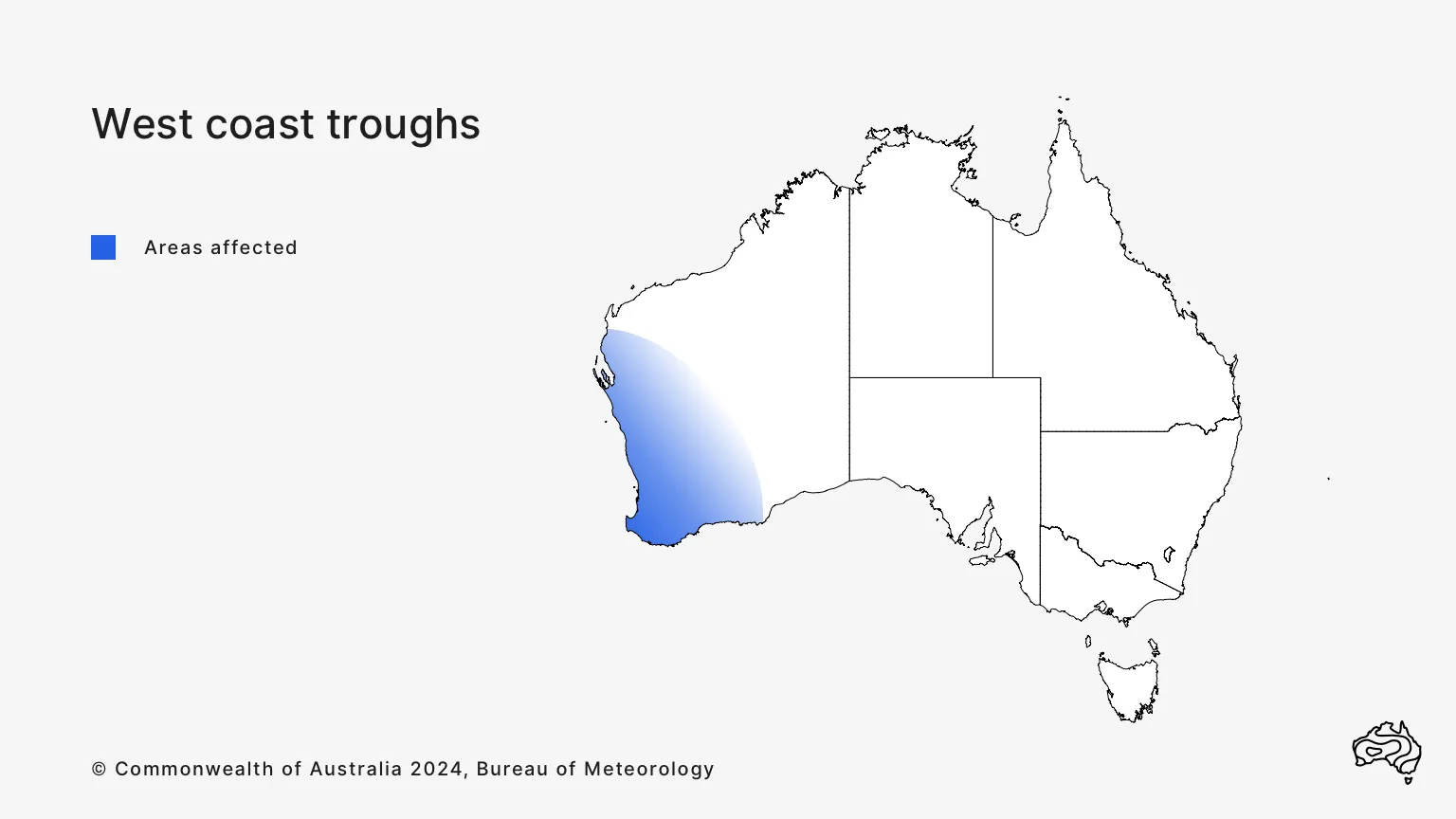
What is the west coast trough?
The west coast trough is a low pressure zone that forms along the southern half of Australia's west coast.
It's a semi-permanent feature of the region's surface pressure pattern in the warmer months. During this time, the west coast trough is the dominant influence on the region's weather.
It is commonly associated with warm and dry conditions.
Timing and duration of a west coast trough
A west coast trough begins to form as the land warms up. They are most common during November to March, but can appear anytime from September to April.
The trough generally lasts from a few days to a week, before moving east across Australia.
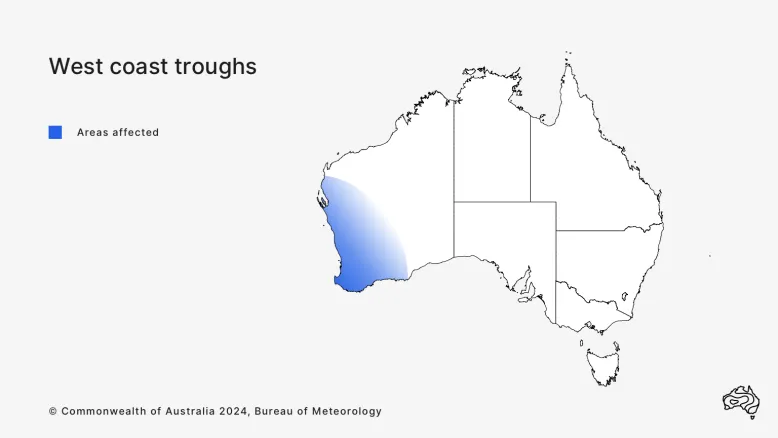
West coast troughs affect the south-east of Western Australia. They are most common from November to March, lasting from a few days to a week.
How a west coast trough develops
A west coast trough forms at the boundary between:
- warm continental easterly winds driven by the subtropical ridge to the south, and
- cooler maritime air from the Indian Ocean.
The trough typically extends north to meet a heat low in the Pilbara region. A heat low is an area of low pressure formed by rising hot air.
The trough can move west off the coast or inland, depending on other weather patterns.
Typical west coast trough sequence
- The trough deepens near the west coast over several days, as winds east of the trough tend warmer north-easterly.
- This deepening is influenced by a strong high pressure system in the sub-tropical ridge, in or south of the Great Australian Bight.
- When there is a cold front south-west of Australia, the trough generally moves east over inland Australia.
- Trough development starts again when a high following the cold front moves south of Australia. Easterly winds re-establish near the west coast.
Similar trough patterns
A similar trough system is the easterly trough in eastern Australia. West coast trough patterns also happen in other parts of the world, for example near the west coast of southern Africa.
How a west coast trough affects Australia
Near Australia's west coast, the trough affects:
- temperatures
- winds
- thunderstorm development.
East of the trough
Depending on the stage of development, areas east of the trough can experience:
- hot days with temperatures above 40° C
- possible thunderstorms, if there is enough moisture in the atmosphere.
West of the trough
There are generally milder conditions, with sea breezes.
Offshore or onshore
The position of the trough depends on other weather patterns. It can change during the day.
For example, the trough may be offshore in the morning then move inland in the afternoon. This often brings strong sea breezes during the day along northern parts of the west coast.
Weather and climate factors related to the west coast trough
Upper level trough
Sometimes the trough interacts with an upper level trough moving over the west coast. This can produce heavy rainfall.
Easterly trough
Easterly troughs feature in the surface pressure patterns of eastern Australia during summer. They bring rainfall to central and inland parts of eastern Australia. Learn about easterly troughs.
Frontal systems
Frontal systems bring rainfall to southern Australia. Cold fronts are the most common in Australia but we can experience warm fronts too. Learn about frontal systems.
Subtropical ridge
The subtropical ridge is a belt of high pressure around the globe in the middle latitudes. It brings dry and stable conditions to large parts of Australia. Learn about the subtropical ridge.