What is a cut-off low?
Cut-off lows are low pressure systems that have broken away from the main belt of low pressure south of Australia. These low pressure systems have been cut off from the prevailing westerly winds.
Cut-off lows may develop when a low pressure system forms on an active cold front. For more about cold fronts, view our Frontal systems page.
East coast lows are a form of intense cut-off low.
Blocking pairs
A cut-off low often develops with a slow-moving or blocking high. This is called a blocking pair.
The cut-off low forms in an unstable easterly flow on the high's northern flank. The low is generally closer to the equator and the high toward the pole.
Areas affected by a blocking pair can have the same weather for an extended period. A blocking pair can extend the life of a cut-off low.
Timing and duration of cut-off lows
Cut-off lows can form at any time. They are most common during autumn and winter.
A cut-off low generally only lasts for a few days. In a blocking pair, they can persist for up to a week.
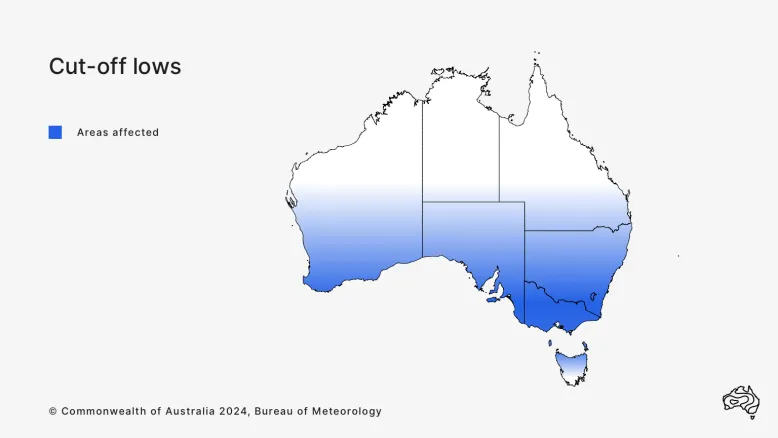
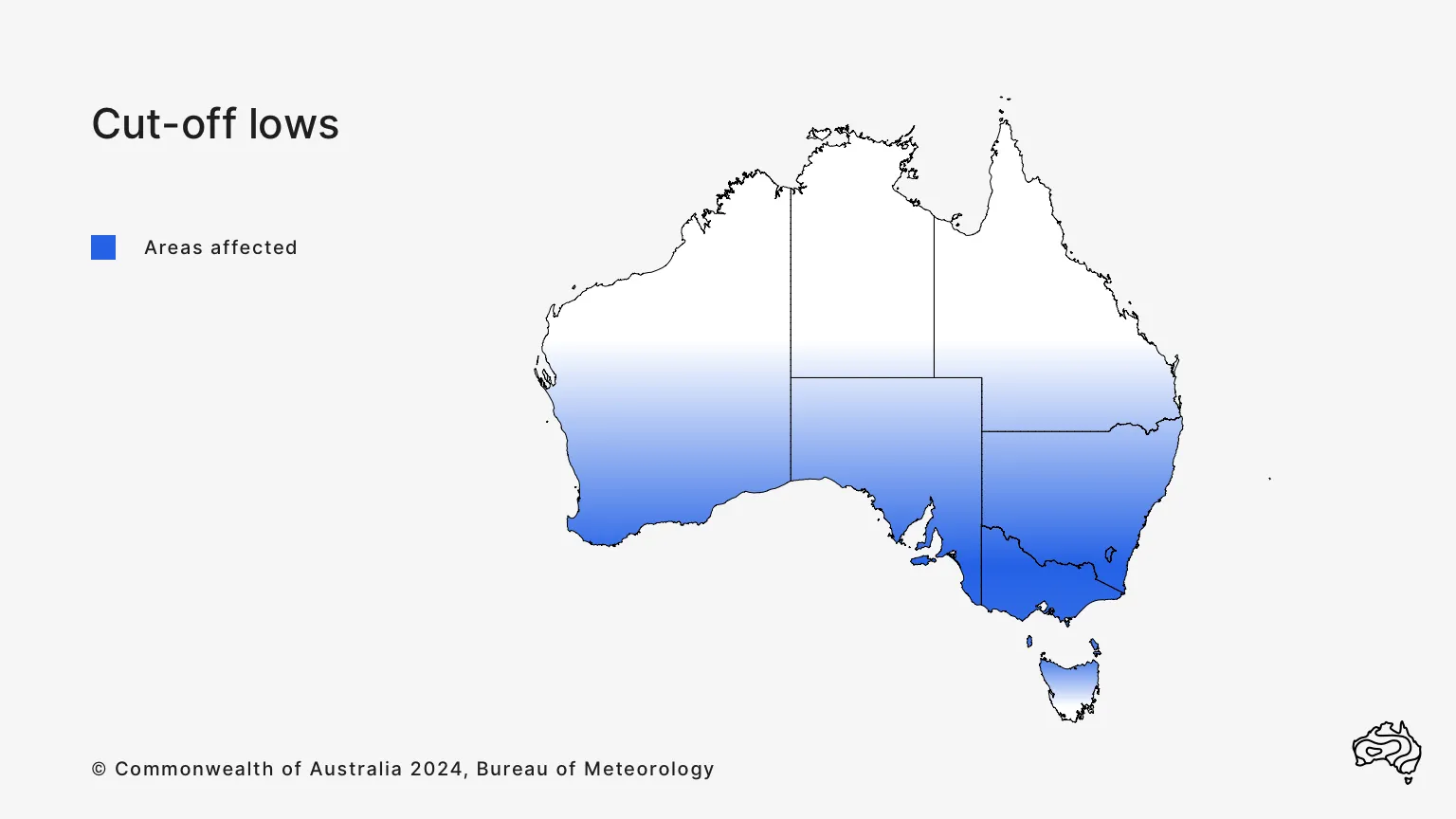
How cut-off lows affect Australia
Cut-off lows enhance rainfall in southern Australia. They can bring:
- sustained rainfall that is often heavy
- strong and gusty winds
- high seas.
Weather and climate factors related to cut-off lows
East coast lows
Along Australia's east coast, intense low pressure systems can bring heavy rainfall and strong and gusty winds to parts of south-eastern Australia. Learn more about east coast lows in our Severe weather knowledge centre.
Upper level troughs
An upper level trough is a trough of low pressure that forms in the upper level of the atmosphere. It can help cloudbands to form anywhere across Australia.